Sensory processing is the way in which our brains interpret and respond to sensory input from our environment. For individuals with autism, sensory processing can be a major challenge, affecting how they perceive and respond to different stimuli. Some individuals with autism may be hypersensitive, meaning they are over-responsive to sensory input, while others may be hypo sensitive, meaning they are under-responsive. This can result in a range of sensory difficulties, from being overwhelmed by loud noises to seeking out certain types of sensory input.
Takeaway:
-
Sensory processing challenges in autism
-
Sensory integration therapy benefits
-
Sensory strategies for daily life
Understanding sensory processing and implementing strategies for support can empower individuals with autism to better navigate the world around them. Here are some key aspects of sensory processing in autism and strategies for support:
Sensory integration:
Sensory integration is the ability to take in and integrate multiple types of sensory input in order to form a complete understanding of the environment. For individuals with autism, sensory integration may be disrupted, making it difficult to process and respond to different types of sensory input. Sensory integration therapy can be a helpful strategy for supporting individuals with autism in this area.
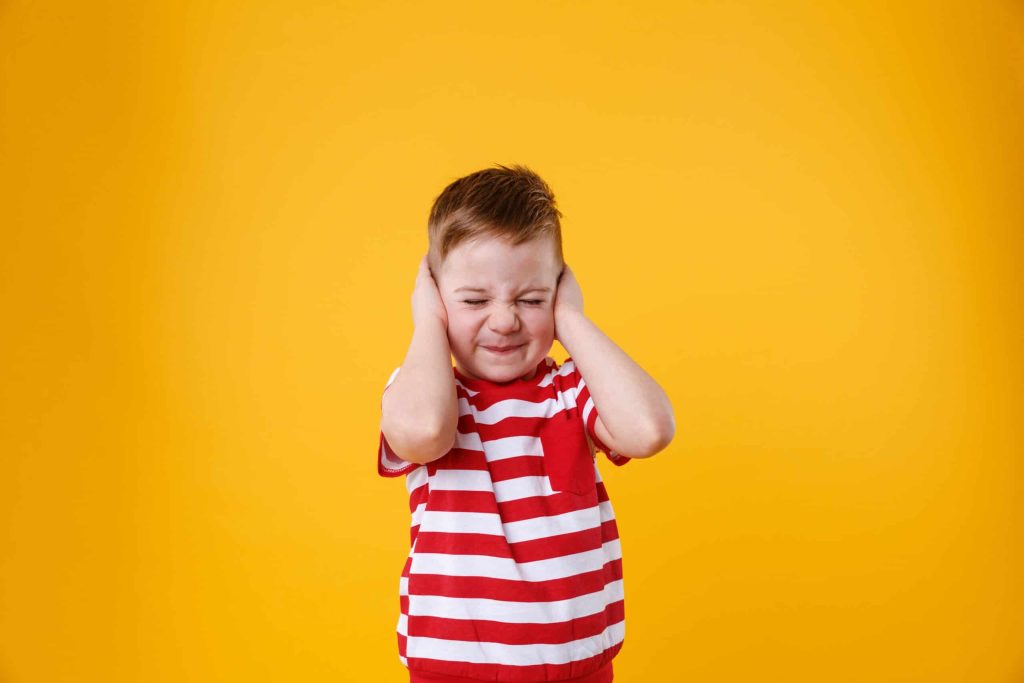

Sensory modulation:
Sensory modulation refers to the ability to regulate and respond appropriately to sensory input. Individuals with autism may struggle with sensory modulation, resulting in over- or under-reacting to certain stimuli. Sensory strategies, such as deep pressure or sensory breaks, can help individuals with autism regulate their sensory input.
Sensory difficulties:
Sensory difficulties in individuals with autism can manifest in a variety of ways, from hypersensitivity to certain types of sensory input to seeking out certain types of sensory input. Identifying and understanding these difficulties can help individuals with autism better manage their sensory experiences and navigate the world around them.
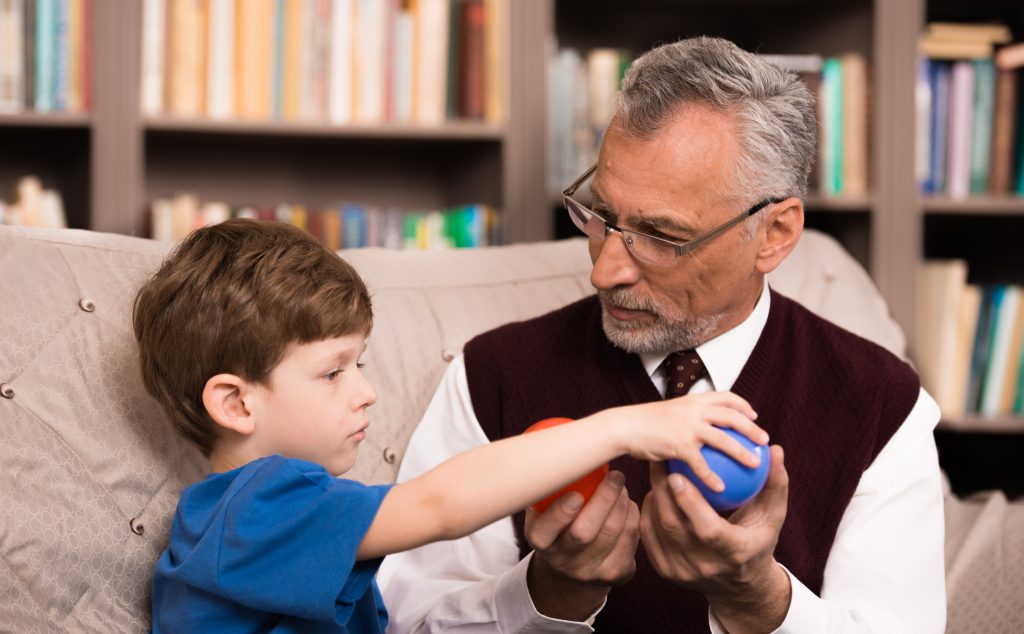

Sensory support:
Providing sensory support can be a crucial strategy for empowering individuals with autism. This may include providing sensory-friendly environments, such as quiet spaces or noise-reducing headphones, or offering sensory-based activities, such as sensory bins or tactile play.
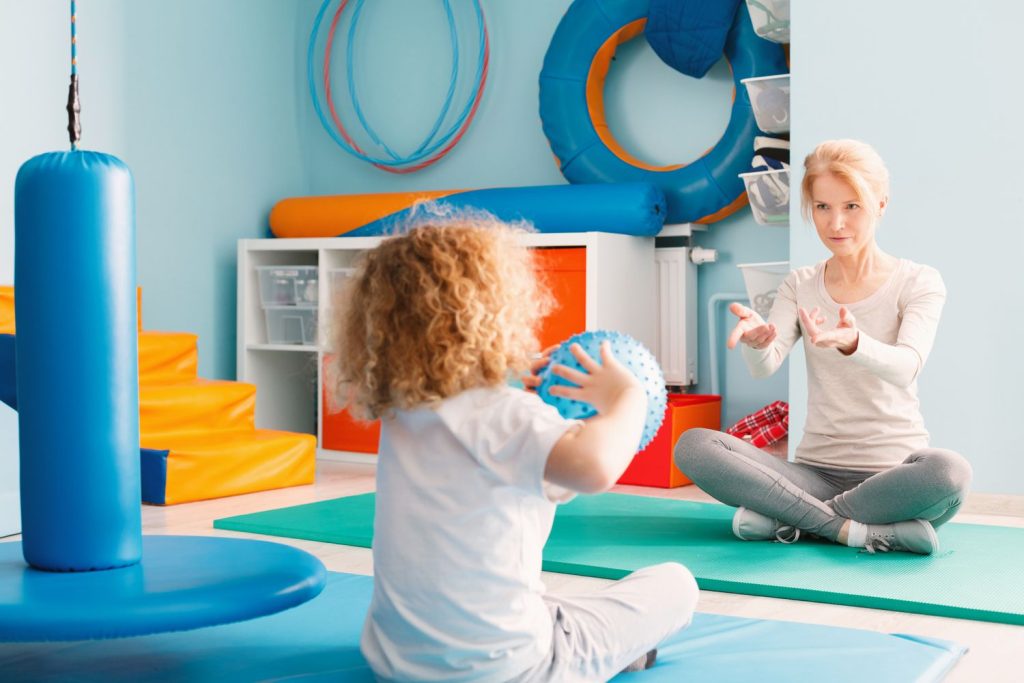

Individualised approach:
It is important to remember that every individual with autism has unique sensory processing needs. A one-size-fits-all approach is unlikely to be effective. Instead, an individualised approach that takes into account the specific sensory needs and preferences of each individual can be more effective.

In conclusion, understanding sensory processing in autism and implementing strategies for support can empower individuals with autism to better navigate the world around them. Sensory integration therapy, sensory strategies, identifying and understanding sensory difficulties, providing sensory support, and taking an individualised approach can all be helpful strategies for supporting individuals with autism in this area. With the right support, individuals with autism can thrive and lead fulfilling lives.














[…] […]